In view of the increasing environmental problems and the demand for ecofriendly agriculture, gardeners and farmers are in search of nature-based alternatives to artificial chemicals. Tea saponin, a natural substance derived from tea seeds (Camellia oleifera or Camellia sinensis), is one of the promising alternatives. Traditionally used in cleaning, aquaculture, and pest control, tea saponin is now making its way into the world of eco-friendly fertilizers - offering benefits for both plants and the soil, while helping reduce environmental impact.
This article will explore what tea saponin is, its unique benefits as a natural fertilizer, how it supports plant growth and soil health, and why it's an eco-friendly choice for modern agriculture.

What is Tea Saponin?
Tea saponin is a natural surfactant found in the seeds of tea plants. It is a member of a class of compounds called saponins, glycosides with soap-like ability for foaming in water. Saponins have antiproliferative activity and are utilized by the plant as a pesticide and disease defense mechanism.
The product is obtained as a byproduct of oil production from tea seeds, hence it is an eco-friendly product utilizing agricultural waste. When processed, tea saponin is typically light brown powder in nature, with active saponin content ranging from 60% to 90% based on processing.

How Tea Saponin Acts in Agriculture
When used in agriculture, tea saponin acts through numerous mechanisms:
- Natural Surfactant Action – Facilitates water penetration into the soil, distributing moisture more equally and nutrient uptake more efficiently.
- Pest and Weed Suppression – Tea saponin is bioactive and has the capacity to repel certain pests in the soil as well as inhibit weed seed germination.
- Soil Structure Improvement – Disrupts surface tension to aerate the soil and improve root zone conditions.
- Microbial Balance – Encourages beneficial soil microbes and inhibits pathological microbes.

Benefits of Tea Saponin for Plants and Soil
1. Strengthens Soil Water Hold and Structure
Soil wellness needs a satisfactory combination of air, water, and nutrients. The surfactant properties of tea saponin lower the water surface tension so that water permeates deep into the soil rather than running over the soil surface. This:
- Prevents waterlogging in clay soils.
- Improves water holding capacity in sandy soils.
- Aids nutrient uptake by roots.
This is especially beneficial in dry regions, where water conservation is crucial.
2. Enhances Nutrient Uptake
Tea saponin can increase the availability of nutrients in the soil. Through enhanced movement of water in the soil profile, dissolved nutrients are distributed evenly so that they become easily accessible to roots of plants. This leads to reduced loss of fertilizer as leachate, thus reducing nutrient pollution.
3. Encourages Healthy Root Development
Roots thrive in humid soil with proper aeration. Tea saponin helps in providing the ideal conditions by preventing compaction and enabling roots to grow long and deep. Healthy roots translate to stronger plants that have improved stress, drought, and disease tolerance.
4. Organic Pest Repellent
One of the lesser-discussed benefits of tea saponin is that it possesses weak pesticidal activity. The compound can deter certain soil-borne pests, nematodes, and disease-fighting fungi without harming beneficial life if used at the correct concentration. This makes it an excellent two-for-one soil conditioner and pest management product.
5. Weed Seed Suppression
Science has proven that tea saponin can suppress germination of certain weed seeds and, therefore, restrict competition for water and nutrients at early stages of crop growth. It is therefore particularly useful in organic farming where synthetic herbicides are not permitted.
6. Supports Beneficial Microorganisms
Healthy soil relies on beneficial bacteria and fungi to break down organic matter, convert nitrogen, and protect against disease. Tea saponin stimulates good microbes while inhibiting the development of harmful species. This balance of microbials enhances the fertility of the soil over time.
7. Environmentally Friendly and Sustainable
In comparison to synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, tea saponin is biodegradable and will not persist in the environment. It is derived from a renewable source - tea seeds - and is often a byproduct of oil extraction, thus utilizing waste farm products and reducing waste in production.
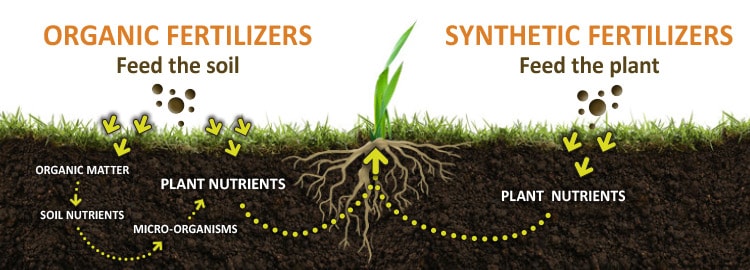
Tea Saponin vs. Synthetic Fertilizers
| Feature | Tea Saponin (Natural) | Synthetic Fertilizers |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Derived from tea seeds (renewable) | Produced from fossil fuels or mined minerals |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, non-toxic | Can cause water pollution, soil degradation |
| Additional Benefits | Improves soil structure, deters pests | Mainly nutrient supply only |
| Cost Efficiency | Long-term soil health reduces inputs | Often requires repeated applications |
While synthetic fertilizers may give quick shots of nutrition to the soil, they can ultimately degrade soil health. Tea saponin, however, nurtures the soil ecosystem toward sustainable production.
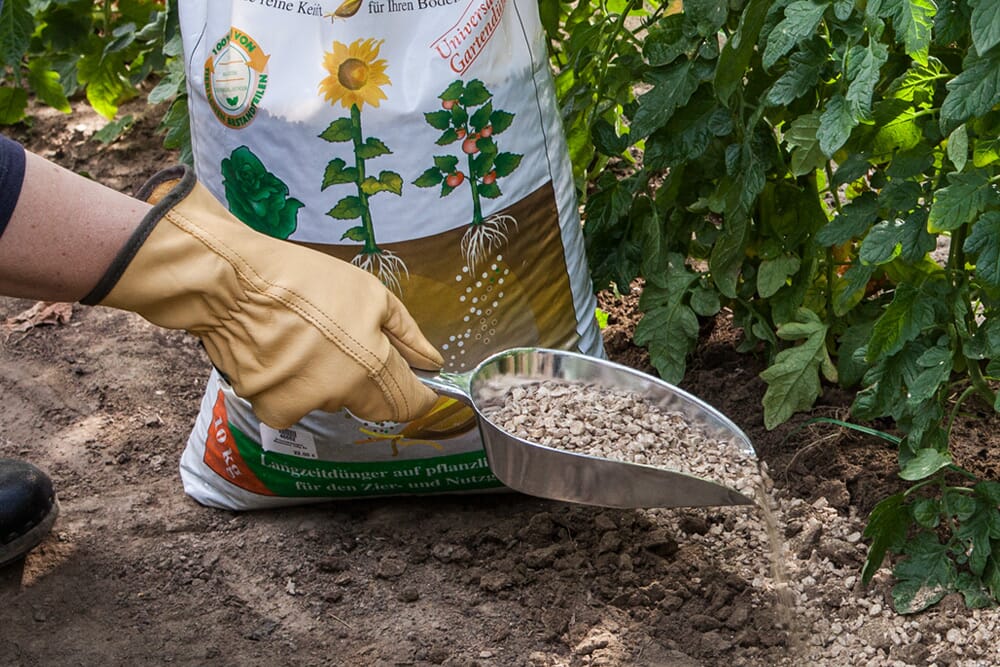

Applying Tea Saponin as a Fertilizer or Soil Improver
Tea saponin can be applied in different ways:
- Soil Amendment Powder – Added to soil before planting to improve structure and water retention.
- Liquid Extract – Sprayed onto soil or leaves to promote nutrient uptake and pest resistance.
- Compost Additive – Added to compost piles to speed up decomposition and promote microbial growth.
Recommended Rates of Application:
- Soil conditioning: 50–100 kg/hectare.
- Liquid spray: 0.05–0.2% solution depending on crop type.
- Pest suppression: Increased concentration (0.2–0.5%), sprayed onto the soil.
(Always use on a test area first, as high concentrations can kill sensitive plants.)

Environmental and Economic Benefits
Changing to tea saponin has many advantages:
- Less reliant on synthetic chemicals – reducing the risk of chemical wash-off into waterways.
- Organic farming accreditation – as it meets many organic input standards.
- Long-term cost-effective – healthier soil requires fewer inputs in the long run.
- Uses agricultural byproducts – promoting circular economy principles.

Scientific Evidence for Tea Saponin Use
The following research has highlighted tea saponin's agricultural significance:
- Wang et al. (2010) determined that tea saponin promoted soil permeability and regulated pest populations in rice paddies.
- Zhao et al. (2015) reported increased nutrient uptake and enhanced root growth among vegetables treated with tea saponin soil amendments.
- Liu et al. (2018) reported a dramatic reduction in nematode populations in tea saponin-amended soils.
These findings support tea saponin's dual role as soil conditioner and green pest repellent.

Final Thoughts: A Good Option for Green Farming
Tea saponin is not just a natural molecule - it's an environmentally friendly, multi-functional, and sustainable solution that can help revolutionize the face of modern farming. Through improving soil health, promoting nutrient uptake, naturally repelling pests, and stimulating sustainable agriculture, tea saponin is a powerful green alternative to chemical fertilizers.
As farmers, gardeners, and agricultural business people opt for greener practices, tea saponin becomes a wise, science-based choice for plant growers wanting healthy crops, strong soils, and a cleaner earth.
References:
Wang, X., et al. (2010). "Application of tea saponin in agriculture." Journal of Agricultural Science, 28(4), 55–60.
Zhao, L., et al. (2015). "Effect of tea saponin on nutrient uptake and root growth." Plant and Soil, 388(1–2), 203–214.
Liu, Y., et al. (2018). "Control of soil nematodes using tea seed meal." Applied Soil Ecology, 124, 45–52.










